In earlier guides, the server-side setup has been completed. Currently, its time to set up with our client-side installation and configuration. Initially, we need to install the client packages by following we need to register with Spacewalk server using “rhnreg_ks” or “rhn_register“.
More Spacewalk related topics are as follows:
- How to install Spacewalk Linux systems management on RHEL and CentOS Linux 7
- How to create Software channels, Repos, Activation keys & sync in Spacewalk Server 2.8
Step 1:
Let’s start to add the required repositories for client packages.
RHEL 6 clients:
Install the client packages from official spacewalk repository for RHEL 6 based Linux client servers. EPEL repo needs to be available to resolve few of dependencies.
# rpm -Uvh https://copr-be.cloud.fedoraproject.org/results/@spacewalkproject/spacewalk-2.8-client/epel-6-x86_64/00742644-spacewalk-repo/spacewalk-client-repo-2.8-11.el6.noarch.rpm # rpm -Uvh http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-6.noarch.rpm
RHEL 7 clients:
We need to add with official client repositories for RHEL 7 based clients too.
# https://copr-be.cloud.fedoraproject.org/results/%40spacewalkproject/spacewalk-2.8-client/epel-7-x86_64/00742644-spacewalk-repo/spacewalk-client-repo-2.8-11.el7.centos.noarch.rpm # rpm -Uvh http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm
Step 2:
Install support program packages for spacewalk clients.
# yum install rhn-client-tools rhn-check rhn-setup rhnsd m2crypto yum-rhn-plugin -y
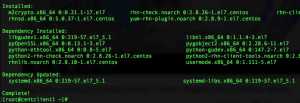
Step 3:
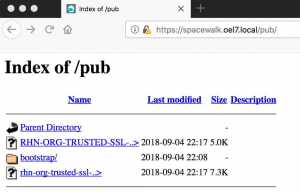
Once performed with client package installation we need to install with Spacewalk’s CA certificate on the client servers to enable SSL communication. To find the CA certificate navigate to Spacewalk’s /pub URL from browser and download it to spacewalk server using curl.
https://spacewalk.oel7.local/pub/
# curl --insecure -O https://spacewalk.oel7.local/pub/rhn-org-trusted-ssl-cert-1.0-1.noarch.rpm # rpm -ivh rhn-org-trusted-ssl-cert-1.0-1.noarch.rpm

Step 4:
Finally, we are good to register our clients with Spacewalk server using the activation key.
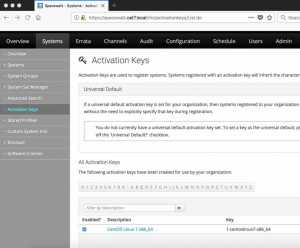
To get the activation key from spacewalk server UI navigate to Systems –> Activation Keys –> copy the key “1-centoslinux7-x86_64”
There are two ways we can register Linux servers with the spacewalk as a client.
- Automated way using the rhnreg_ks command with an activation key.
- The manual method using rhn_register using TUI.
Option 1:
Use the command with URL, CA certificate and activation key.
# rhnreg_ks --serverUrl=https://spacewalk.oel7.local/XMLRPC --sslCACert=/usr/share/rhn/RHN-ORG-TRUSTED-SSL-CERT --activationkey=1-centoslinux7-x86_64

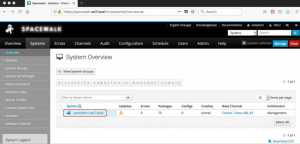
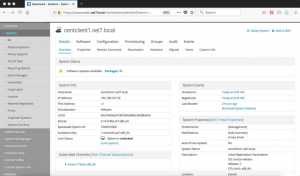
Client-server has been registered with the spacewalk server.
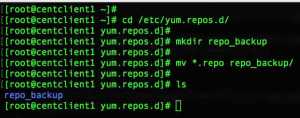
Clear the default repo file from /etc/yum.repo.d/ by moving into any one of the directories.
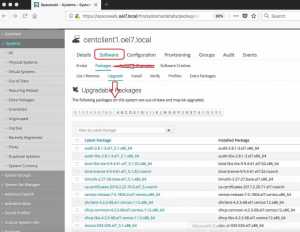
List the available repositories using “yum repolist all” command.

Option 2:
We can register a client using “rhn_register” command which will prompt to enter the admin username and password. This is a manual method which can be done in TUI mode by following NEXT –> NEXT –> NEXT –> FINISH. It’s good to follow option 1 for registering a client by automating it.
# rhn_register
If clients do not reflect the available updates in Spacewalk UI force the client to sent information by running.
# rhn_check
That’s it we have registered a Linux server with the spacewalk server as a client to receive packages and updates.
Conclusion:
To manage the client machines from the spacewalk, we have done with simple installation steps in a Linux server and made it as a client by subscribing with Spacewalk server. It provides us with wide support for provisioning, managing configuration, running schedules and much more. Let us see more topic on the spacewalk in upcoming articles, subscribe to our newsletter by submitting your email ID at the bottom of this page.

How to unregister client in command line from spacewalk.
Debian and Ubuntu
Thank you for your article 🙂 It’s really helpful, could you please explain how to create
channel and repository for Debian ?